About the project
REACHOUT is a pioneering initiative under the European Green Deal that aims to transform urban resilience against climate challenges.
With a focus on city-oriented climate services, REACHOUT collaborates with a diverse range of European cities to co-create tailored climate information tools. These tools assist cities in navigating physical hazards, setting ambitious climate goals, and fostering a climate-resilient future. These include the project’s co-creation hubs, which are a ‘melting pot’ of city representatives and tool developers who work together to innovate climate services that are valuable, accessible and user-friendly.
From Amsterdam's focus on real estate sector risks to collaborative efforts in cities like Lillestrøm, Cork, and Milan, REACHOUT is a testament to the power of collective innovation in tackling climate change.
Description of success
REACHOUT has achieved significant milestones in enhancing urban climate resilience. By closely working with knowledge partners, the project has co-developed tools that advance technical capabilities and improve decision-making for cities.
The success story is also highlighted by the REACHOUT learning programme, which has supported the building of adaptation capacity and fostered a sense of community among stakeholders. The project’s innovative approach to climate science communication, through the creation of climate stories, has pioneered a novel method of engaging citizens with scientific outputs. Furthermore, the development of the REACHOUT toolkit encapsulates the project's holistic approach, offering a suite of tools to support European cities in their climate adaptation journeys.
Highlights
The co-creation process has led to the development of over 10 applications, enhancing the integration of tools with different platforms and data, and providing a wide range of tool combinations.
The project has successfully implemented climate stories as a tool for putting scientific results into context to enhance local engagement and understanding.
Business models from both user and developer perspectives have been identified, paving the way for further sustainable climate service solutions.
The innovative Triple-A Toolkit has been introduced, guiding cities through Analysis (of existing and future risk), Ambition (with respect to climate resilient development), and Action phases to address their unique climate challenges.
Outputs
REACHOUT has published several resources to complement their recent successes.
Their Triple-A Toolkit, which is available online, is designed to help urban planners and adaptation practitioners in European cities, integrate climate resilience into their work. The toolkit supports users’ understanding of the risks and opportunities associated with climate change and helps them to prioritise different climate adaptation measures. The end goal is to enable users to develop effective adaptation strategies for their city.
REACHOUT has also released a series of online training modules as part of its learning program for city hubs. The program teaches participants about climate resilient development and imparts skills and tools that can be used to improve resilience in each city hub using the Triple-A approach.
The first round of climate stories has been published and is available to read in this report. Climate stories aim to build a bridge between science and society through a novel and engaging approach to science communication.
REACHOUT has also published a policy brief that will help guide policymakers and city planners in their approach to adapting to climate change. It expresses the urgent need to integrate climate services into cities’ municipal planning and outlines how this can be achieved through identifying barriers and solutions.
Impact
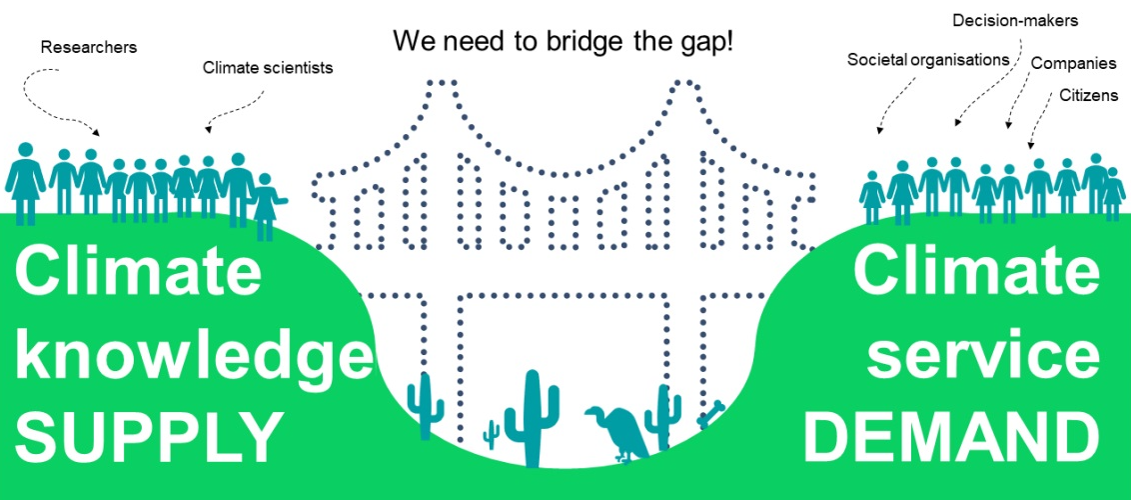
REACHOUT has significantly contributed to contextualising climate adaptation challenges within the broader framework of climate-resilient urban development. This approach has enabled cities to simultaneously address multiple challenges, enhancing the relevance and impact of climate services. The project's toolkit and strategic planner have played a crucial role in guiding cities through the maze of climate services, ensuring that they select and use the tools most suited to their specific needs. Furthermore, the role of liaisons has been instrumental in bridging the gap between city stakeholders and knowledge partners, improving communication and aligning with the project's aims.
Lessons
The Triple-A approach (Analysis, Ambition and Action) has been successfully implemented and has enabled cities to overcome the barrier of a crowded and unclear landscape of climate services. The Toolkit gives cities the power and understanding to effectively use tools to suit their specific needs.
Cities can rarely focus on one goal and often need to balance a variety of priorities with limited resources. It is therefore not common for climate adaptation to be the primary focus of their objectives. REACHOUT’s broad climate-resilient perspective allows cities to identify links between goals and map out their different ambitions, with climate adaptation a consideration throughout.
Involving cities as partners to the projects has encouraged increased engagement and therefore led to more success. Communication between various city stakeholders can often cause a bottleneck in planning actions, so REACHOUT has solved this by acting as a point of liaison. Their climate stories increase the accessibility of scientific information and therefore further improve communication between stakeholders.
Other information
REACHOUT will continue to support their city hub partners to integrate climate resilience and adaptation into daily life. The project has identified a need for cities to increase communication about climate change and its effect on citizens, as well as other departments within their governance that do not focus on the environment. The project also has ambitions to expand its work to all cities in Europe. However, there will be significant challenges associated with this. REACHOUT will fine-tune its toolkit and conduct work to better understand potential barriers to upscaling.